The Bayesian cable curl is not like another biceps train.
For starters, the shape is exclusive: you curl a cable one arm at a time along with your arm behind your physique and your again to the cable stack (therefore why folks typically confer with it as “the face-away cable curl” or “behind-the-back cable curl”).
It additionally trains your biceps whereas totally stretched and applies stress to your muscle tissue all through all the vary of movement—one thing you don’t get with free-weight options. Crucially, these sides make it notably efficient for constructing biceps mass.
So, if you wish to perceive tips on how to carry out the Bayesian curl, why it’s so efficient, and tips on how to keep away from errors folks typically make whereas performing the train, this text is for you.
How you can Do the Bayesian Cable Curl
To grasp Bayesian cable curls, break up the train into three elements: arrange, curl, and descend.
1. Arrange
Set the pulley on a cable machine to the bottom setting and fasten a single-handle attachment. Place your ft subsequent to the pulley, seize the deal with in your proper hand, after which flip your again to the cable stack.
Step 1-to-2 ft ahead along with your left foot, place your left hand in your left thigh for stability, and lean barely ahead.
Rotate your proper wrist so your palm faces ahead, place your proper elbow about an inch behind your proper lat, and let the cable pull your proper arm straight so you are feeling your proper biceps stretch.
2. Curl
With out shifting your proper elbow ahead, bend your proper elbow to twist the deal with towards your proper shoulder.
3. Descend
Reverse the motion and return to the beginning place.
Right here’s how correct Bayesian cable curl kind ought to look whenever you put all of it collectively:



Bayesian Cable Curl Advantages
They’re ideally suited for constructing biceps mass.
For an train to be efficient, it should place numerous stress on the muscle you’re making an attempt to coach. It additionally helps if it trains the muscle when totally stretched.
The issue with most biceps workout routines is that they fall quick in these areas.
Workouts like dumbbell and barbell curls place little stress on the biceps on the backside and prime of every rep. And since your elbows keep at your sides throughout each workout routines, they don’t prepare the biceps when stretched. The biceps are solely totally lengthened when your elbows are behind your physique.
The Bayesian curl fixes these points. By performing the train with a cable and turning away from the cable stack, you preserve stress in your biceps all through all the vary of movement. Holding your elbow barely behind your torso as you carry out the train additionally ensures the biceps totally stretch.
These elements make the Bayesian curl ideally suited for constructing biceps mass.
It trains your biceps unilaterally.
The “face-away curl” is a unilateral train, which implies it means that you can prepare one aspect of your physique at a time.
That is useful as a result of unilateral workout routines . . .
Might allow you to carry extra complete weight than you possibly can with some bilateral workout routines, which can assist you acquire extra muscle over time
Enable you develop a higher mind-muscle connection along with your biceps since you solely have to deal with one aspect of your physique at a time
Enable you appropriate muscle imbalances, as a result of either side of your physique are pressured to carry the identical quantity of weight (one aspect can’t “take over” from the opposite)
It maximizes biceps development.
Your biceps are closely concerned in “pulling” workout routines, such because the lat pulldown, row, and pull-up.
Nevertheless, analysis reveals that if you wish to maximize biceps growth, doing compound pulling workout routines isn’t sufficient—you must do biceps isolation workout routines, too.
There are two causes for this:
Biceps isolation workout routines just like the Bayesian cable curl can help you prepare your biceps in several methods—at completely different angles and thru completely different ranges of movement—which most likely produces extra balanced and full development than doing simply 2 or 3 pulling workout routines.
Biceps isolation workout routines can help you prepare your biceps when it’s not sensible to take action with a compound train. As an illustration, after a number of units of pulling workout routines, your lats, traps, and rhomboids will most likely be bushed, however your biceps could also be comparatively contemporary. Including a number of units of curls ensures they’re adequately stimulated, which is significant to maximize development.
Bayesian Cable Curl: Muscle mass Labored
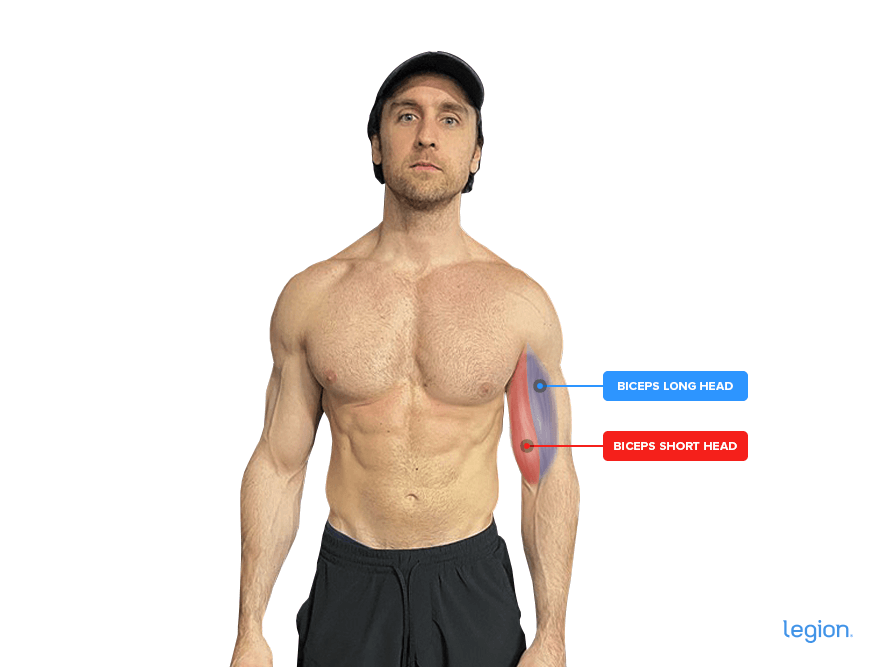
The primary muscle tissue labored by the Bayesian cable curl are the biceps brachii (or “biceps”), the two-headed muscle tissue on the entrance of your higher arms, between your shoulders and elbows.
Right here’s how the biceps look in your physique:

Frequent Bayesian Cable Curl Errors
Letting the cable pull your arm too far backward.
If the burden pulls your arm to date backward that your elbow is a number of inches behind your torso, you lose stress in your biceps on the prime and backside of every rep, which reduces the train’s effectiveness. Repair this by holding your elbow stationary and barely behind your lat all through every rep.
Lifting an excessive amount of weight.
Attempting to carry an excessive amount of weight on the Bayesian curl makes the train troublesome to carry out accurately—the cable will pull you backward, you’ll have hassle coaching by means of a full vary of movement, and also you’re extra more likely to have interaction different muscle teams to “cheat” the burden up—all of which makes the train much less efficient.
Keep away from this error by choosing a weight that means that you can carry out the train with correct kind, by means of a full vary of movement, and with out different muscle tissue helping your biceps.
Hitting your wrist with the cable.
If the cable hits your wrist as you curl the burden up, you’re not leaning far sufficient ahead. Right this by bending ahead barely additional on the hips.
FAQ #1: What’s the distinction between the incline curl and Bayesian curl?
The primary distinction between the Bayesian cable curl and incline dumbbell curl is execution: within the Bayesian curl, you prepare every arm independently utilizing a cable machine and whereas standing, whereas within the incline curl, you prepare each arms concurrently utilizing dumbbells and whereas seated.
Nevertheless, each workout routines work your biceps equally and comparably, so you should utilize them interchangeably.
FAQ #2: What’s the second arm in a Bayesian curl?
In weightlifting, a second arm is the gap between the joint and the road of power utilized throughout an train. It determines how a lot leverage or torque you need to produce to maneuver the joint.
For instance, whenever you carry out a dumbbell curl, the second arm is the gap out of your elbow to the burden, which determines how a lot power your biceps have to exert to carry the dumbbell.
One of many major benefits of the Bayesian curl is that it maintains a constant second arm all through the vary of movement, which helps to maintain fixed stress on the biceps. That is not like conventional dumbbell or barbell curls, the place the second arm reduces stress on the prime and backside of every rep.
FAQ #3: Do Bayesian curls work the lengthy head?
Sure, Bayesian curls place your arm behind your physique, which helps you emphasize the biceps lengthy head greater than workout routines that place your elbows beside or in entrance of your torso.
Moreover, you supinate your wrists (flip your palms upward) in the course of the Bayesian cable curl, which additionally helps you emphasize the lengthy head.
+ Scientific References
Schoenfeld, Brad J. “The Mechanisms of Muscle Hypertrophy and Their Software to Resistance Coaching.” Journal of Power and Conditioning Analysis, vol. 24, no. 10, 2010, pp. 2857–72, https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181e840f3.
Oranchuk, Dustin J., et al. “Isometric Coaching and Lengthy-Time period Variations: Results of Muscle Size, Depth, and Intent: A Systematic Evaluation.” Scandinavian Journal of Medication & Science in Sports activities, vol. 29, no. 4, 13 Jan. 2019, pp. 484–503, https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13375.
Maeo, Sumiaki, et al. “Triceps Brachii Hypertrophy Is Considerably Higher after Elbow Extension Coaching Carried out within the Overhead versus Impartial Arm Place.” European Journal of Sport Science, 12 July 2022, pp. 1–26, https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2022.2100279.
Jakobi, Jennifer M., and Philip D. Chilibeck. “Bilateral and Unilateral Contractions: Potential Variations in Maximal Voluntary Drive.” Canadian Journal of Utilized Physiology, vol. 26, no. 1, Feb. 2001, pp. 12–33, https://doi.org/10.1139/h01-002.
Janzen, Cora L., et al. “The Impact of Unilateral and Bilateral Power Coaching on the Bilateral Deficit and Lean Tissue Mass in Submit-Menopausal Ladies.” European Journal of Utilized Physiology, vol. 97, no. 3, 28 Mar. 2006, pp. 253–260, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-006-0165-1.
Costa, Bruna Daniella de Vasconcelos, et al. “Does Performing Completely different Resistance Workouts for the Identical Muscle Group Induce Non-Homogeneous Hypertrophy?” Worldwide Journal of Sports activities Medication, vol. 42, no. 09, 13 Jan. 2021, pp. 803–811, https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1308-3674.
Landin, Dennis, et al. “Actions of the Biceps Brachii on the Shoulder: A Evaluation.” Journal of Medical Medication Analysis, vol. 9, no. 8, 2017, pp. 667–670, https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr2901w.
Jarrett, Claudius D., et al. “Anatomic and Biomechanical Evaluation of the Quick and Lengthy Head Elements of the Distal Biceps Tendon.” Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgical procedure, vol. 21, no. 7, July 2012, pp. 942–948, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2011.04.030.





















