Researchers in Germany just lately printed a kind of research that, every now and then, make me query my core beliefs. I’m a complement skeptic, however I attempt to not let that identification stop me from assimilating new information. And if there’s one complement whose attainable advantages I’ve been on the fence about in recent times, it’s vitamin D.
The brand new examine, which seems within the European Journal of Utilized Physiology, is a part of a serious initiative to enhance the efficiency of German elite athletes. A analysis group led by Sebastian Hacker of Justus Liebig College in Giessen studied 474 athletes on German nationwide groups in a spread of sports activities together with hockey, desk tennis, and three-on-three basketball. They examined vitamin D ranges and measured (amongst different outcomes) handgrip power.
Right here’s the cash shot:
This graph reveals handgrip power as a perform of 25(OH)D ranges, which is how vitamin D standing is assessed within the blood. The 2 dashed strains point out the thresholds between vitamin D deficiency (beneath 20 ng/mL), insufficiency (between 20 and 30 ng/mL), and sufficiency (above 30 ng/mL). There have been lengthy debates on the place these thresholds must be set, however that’s the present pondering. Word that you simply’ll generally see 25(OH)D ranges expressed in nmol/L; to get to these models, multiply the values above by 2.5.
The important thing level: there’s a transparent slope to the road. Greater ranges of vitamin D are related to stronger grip power, which in flip has been related to well being, longevity, and (much less clearly) athletic efficiency. For each 1 ng/mL enhance in 25(OH)D, handgrip power will increase by 0.01 N/kg, which implies that going from 20 to 30 ng/mL ought to increase your power by about three %.
The Case for Vitamin D Dietary supplements as a Efficiency Help
Vitamin D performs roles in a complete bunch of physique programs, together with bone well being, immune perform, and—maybe most notably for athletes—muscle efficiency. In case you’re actually poor in vitamin D, there’s little doubt it is best to get your ranges up. However the proof within the “merely inadequate” vary is much less clear, even on this information. In case you took all of the values beneath 20 mg/mL out of the evaluation, would there nonetheless be a relationship between vitamin and handgrip power? It’s not clear.
This isn’t the primary time researchers have proven a relationship between vitamin D and power. In truth, a scientific assessment printed a couple of months in the past pooled information from 28 research with 5,700 contributors and concluded that there’s a constructive relationship between vitamin D ranges and quadriceps power. At the least, that’s the headline consequence—however whenever you look nearer, it’s much less convincing. The constructive relationship was for quad power when contracting the muscle at a particular velocity of 180 levels per second. However there was no relationship at a slower velocity of 60 levels per second. Worse nonetheless, there was a damaging correlation for maximal contractions towards an immoveable power: greater vitamin D ranges had been related to smaller max power.
In different phrases, we shouldn’t be too fast to imagine the brand new German information is definitive. As a substitute, it’s one other information level in an ongoing debate. One other assessment, printed in September by researchers from Japan, finds “blended outcomes” in research on the connection between vitamin D ranges and muscle mass and power.
Causation or Correlation?
Even when we finally conclude that there’s a constructive relationship between vitamin D ranges and power, it doesn’t essentially comply with that we should always all begin popping vitamin D tablets. To start with, there’s the potential of reverse causation. People who find themselves sturdy and wholesome could select to spend extra time exercising outside, which in flip could produce greater vitamin D ranges. That’s truly one of many strengths of the brand new German examine: since all the themes had been elite athletes, we are able to assume that they’ve comparable ranges of basic health and bodily exercise.
There can also be confounding elements. Again in 2019, Outdoors contributing editor Rowan Jacobsen wrote a stunning article during which he argued that the advantages of daylight lengthen past merely elevating vitamin D ranges, most notably in triggering the discharge of nitric oxide out of your pores and skin into your bloodstream. If that’s the case, then taking vitamin D dietary supplements gained’t essentially repair no matter issues are related to lack of sunshine.
What we actually need are intervention research, the place we give additional vitamin D to folks and see in the event that they get stronger. And we don’t need topics who have already got ample ranges of vitamin D, as a result of they stand to profit much less; as an alternative we wish folks with inadequate ranges. That’s what one other new examine, this one from Estonia, did.
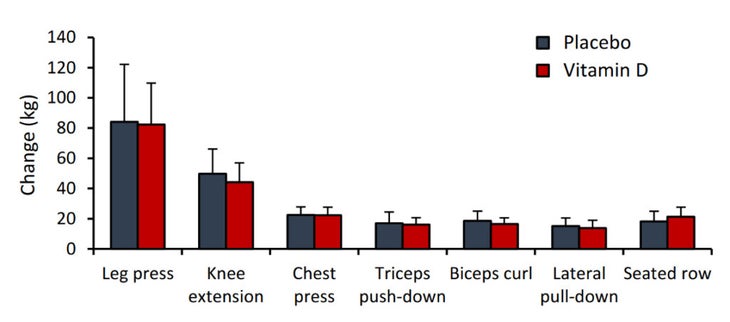
The Estonian researchers took 28 volunteers with “inadequate” 25(OH)D ranges within the low 20s mg/mL. Half of them obtained a placebo, and the opposite half took 8,000 IU per day of vitamin D, which finally obtained their 25(OH)D ranges as much as a wholesome 57 ng/mL. Each teams did 12 weeks of resistance coaching, however there have been no discernible variations of their outcomes, which had been printed within the journal Vitamins. Listed here are the good points in one-rep most for numerous workouts for the 2 teams:
In truth, the additional you dig into the literature, the much less convincing the info seems to be for vitamin D as an athletic complement. For instance, there was a 2019 assessment within the Journal of the Worldwide Society of Sports activities Vitamin that discovered no vital advantage of vitamin D supplementation on muscle power however a pattern in the correct path. However even that weak discovering was tainted by “key errors within the analytical strategy,” in keeping with a reanalysis printed final 12 months: the true impact is near zero.
In fact, vitamin D’s deserves as an athletic complement are distinct from its potential for extra basic well being functions. May it’s that taking vitamin D dietary supplements helps stop most cancers, coronary heart illness, or sort 2 diabetes; will increase bone density; or reduces your threat of falls? No, no, no, no, and no, in keeping with a abstract of the prevailing proof from human trials printed in 2021. Greater than 60 Mendelian randomization research, which use genetic information to divide folks into pseudo-randomized teams with excessive or low vitamin D ranges, have usually discovered no distinction in well being outcomes.
Put all of it collectively and the general case for taking vitamin D dietary supplements doesn’t look very compelling to me—assuming, that’s, that you simply don’t have a real deficiency. Defining that threshold is the tough half. Is it beneath 20 ng/mL, which well being authorities think about poor? Is it beneath 30 ng/mL which they label inadequate? Is it someplace greater or decrease or in between? I’m unsure, so for now I’ll hedge my bets: regardless of all my skepticism, I’m going to rearrange to get my ranges examined at my subsequent physician’s appointment.
For extra Sweat Science, be part of me on Threads and Fb, join the e-mail publication, and take a look at my forthcoming e book The Explorer’s Gene: Why We Search Massive Challenges, New Flavors, and the Clean Spots on the Map.





















